At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Occiput?
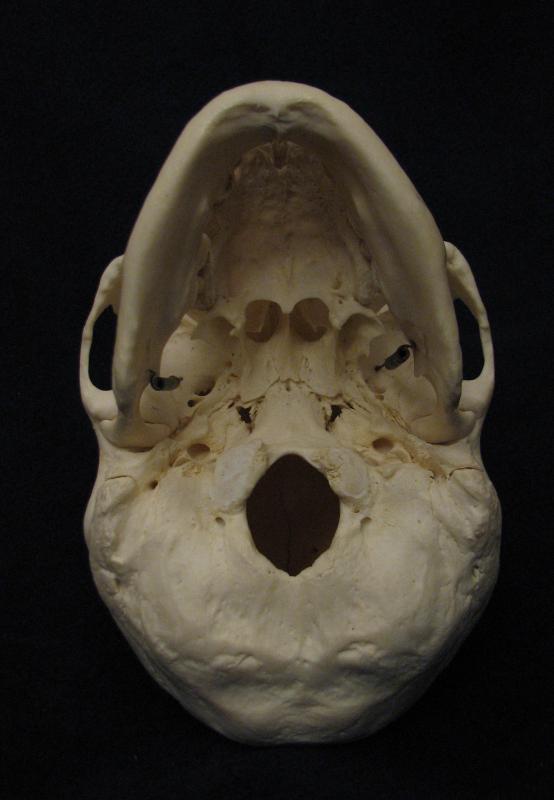
The occiput is the section on the cranium or skull bone located at the back of the head near the base of the neck. This bowl-shaped bone has an opening called an aperture called the foramen magnum. This cavity allows the brain to communicate with the rest of the body.
Inside the foramen magnum of the occiput there are a number of structures running through it, such as the medulla oblongata and cranial nerves. The medulla oblongata is the lower portion of the brain stem which connects the brain to the spinal cord. The cranial nerves, originating in the cranium, are the thread-like fibers that receive electrical signals. These nerves then filter the impulses to the appropriate area so the body can react to external stimuli.

There are also projections and ridges located on the occiput bone. Just behind the foramen magnum is a rounded plated called the squama occipitalis. The outside of the squama is where several cervical muscles attach the head to the neck. Inside the squama there are four channels called fossae which house the cerebellum. The cerebellum of the brain is responsible for controlling movement.
In front of the foramen magnum there is dense area referred to the basilar portion of the occiput. This area joins the occiput with the sphenoid bone, which help define the openings for the eyes. As bones age, the occiput and sphenoid harden together to form one bone.
The lateral aspects of the occiput are located on either side of the head and form the sides of the foramen magnum. There are condyles or rounded areas on the sides of the occipital bone that connect the vertebral or spinal bones of the neck to the head. At the bottom of each condyle there is a small channel or canal that houses the hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve.
There are two angles on the curved bone known as the occiput. The superior or uppermost angle attaches to the parietal bones which create the sides of the head. These bones then join together at the top of the skull. As the bone ages the parietal bones fuse together.
The lower or inferior angles of the occiput house the transverse sinuses. The transverse sinuses are opening that allow for blood to flow from the head towards the nose. These lower sections are also the attachment site for the mastoid. The mastoid is a cone-shaped ridge where muscles of the jaw and neck fasten to the head.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:










Discuss this Article
Post your comments