At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is the Intraperitoneal Cavity?
The intraperitoneal (IP) cavity is an area inside the abdomen completely surrounded by the peritoneum, a thin, strong membrane that provides support for abdominal organs. A number of the abdominal viscera are located inside this wrapping. Other structures, like the kidneys and bladder, are on the outside, but may lie adjacent to the peritoneum. Anatomically, it can be important to distinguish between this and other areas of the abdomen for activities like patient assessment, surgeries, and injections.
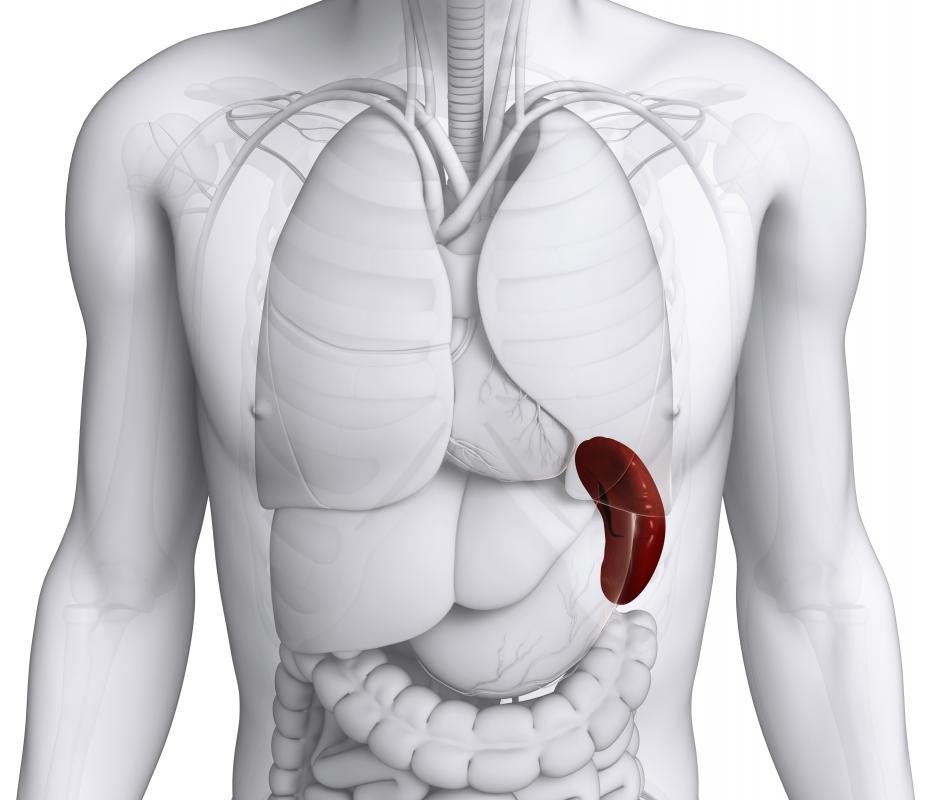
Digestive organs like the stomach and intestines are located inside the intraperitoneal cavity, along with the liver and spleen. They are supplied with a rich array of blood vessels and connective tissue keeps them anchored in place. Organs including the bladder, kidneys, and reproductive tract are located outside. Anatomically, structures like the kidneys are known as retroperitoneal, because they lie behind the intraperitoneal cavity.

Injuries to the abdominal viscera can result in leaks inside the intraperitoneal cavity, which can contribute to swelling, infection, and inflammation. It’s also possible to tear through the connective tissue and create a link between this space and the rest of the abdomen. Cancers and fistulas can push through the peritoneum and invade surrounding tissues, potentially causing severe complications for the patient. For instance, bladder cancers may burst through the membrane and into the intestines.

In surgery, procedures involving the intraperitoneal cavity require the surgeon to work through an additional layer of connective and protective tissue, and they must take care when closing the wound to avoid injuries to the patient. Adhesions, bands of connective tissue that form where they do not belong, are of particular concern. They can potentially interfere with the abdominal viscera and cause complications after surgery, making it critical to proceed cautiously to minimize scar tissue and reduce risks for the patient. Medical imaging may be recommended after surgery to confirm that the incision site is healing and to check for issues like buildups of fluid that might not be readily apparent from external examinations.

Intraperitoneal injection, or IP injection, is a method of drug delivery used for some medications. Most commonly, it’s employed with small animals, particularly those used in research. IP injection can provide a fast method of delivery for fluids or medications if the patient has no suitable blood vessels. It is also used in some forms of cancer therapy in humans, where the intraperitoneal cavity is actually washed in chemotherapy medications to kill cancer cells and increase the chance of survival.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments