At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Corpus Striatum?
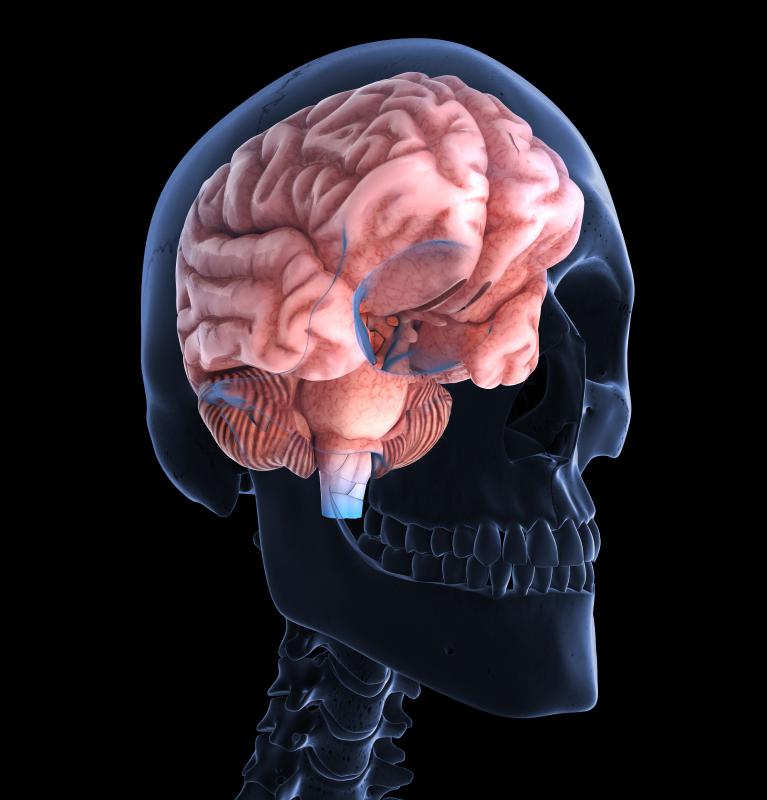
The corpus striatum, or simply striatum, is a structure located in the forebrain in humans and many other animals. It is part of the basal ganglia, a group of structures responsible for controlling movement that also play a role in motivation and rewards. This area of the brain is involved in movement disorders like Parkinson's disease. Research continues to be conducted into the structure and its function in the brain.
This structure is buried deep within the forebrain. The term “corpus striatum” means “striped body” and is a reference to its striped appearance. Different types of tissue are present in layers, making the structure appear to be striped in gray, white, and other colors like cream in a healthy brain. It can only be seen by dissecting the brain, although medical imaging studies can be used to approximate its shape, size, and appearance without disrupting the brain tissue.

The caudate, putamen, and internal capsule are all part of the striatum, and the structure is supplied with blood by the striate artery. It includes very dense bundles of motor neurons and is vulnerable to damage due to strokes and diseases that create lesions in the brain. Because so many functions are concentrated in this small area, it is a devastating location to receive a brain injury as a result of disease.

In healthy individuals, the corpus striatum regulates movement with the assistance of dense bundles of motor neurons and associated neurotransmitters. In people with movement disorders, the signals between neurons are interrupted. Some people may have jerky or erratic movements, tremors, or involuntary movements. Others may have difficulty moving at all as a result of damage to this part of the brain.

The striate arteries are narrow and can be the site of strokes, including both hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, characterized by bleeding and oxygen deprivation, respectively. Treating strokes in this area of the brain is challenging due to the buried nature of the arteries. The area can also be attacked by demyelinating diseases and other conditions that create plaques and lesions in the brain and central nervous system. Lesions erode neurons, interfere with nerve conduction, and can cause significant impairment. Although the brain is adaptable and capable of rewiring many pathways over time, it needs an alternate route for these new pathways, and one is not always available when the damage is located in this area of the brain.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
Reading about the basal ganglia's function of play a role in motivation and rewards because that goes to the core of what I do every day as a therapist. I am constantly weighing rewards and the work that needs to be accomplished to keep motivation and stave off frustration.
It is silly, but I never thought of a specific part of the brain being responsible for this functioning.
As soon as I did though, I realized that if someone's basal ganglia was impaired in that specific area then it would be difficult to reward and maintain motivation because those connections would be there, right?
I wonder if there are any documented cases of such...
Post your comments