At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is Serous Otitis Media?
Serous otitis media is a disorder that typically is characterized by fluid retention in the middle ear chamber. A prior ear infection or an upper-respiratory infection can be a common cause of this condition. The disorder often is seen in younger children, although adults may develop it, as well. One might experience hearing difficulty due to fluid accumulation in the middle ear. If the problem persists, antibiotics may be recommended; surgery could be performed in some cases to drain away the fluid.
This condition also is referred to as otitis media with effusion. Serous otitis media may be acute or chronic if it persists for months. It could cause a feeling of pressure in the ear and may affect one’s hearing as the accumulated fluid tends to impede transmission of sound vibrations. This can interfere with speech comprehension. In the case of children, the condition might impact language advancement, learning, and conduct.

Sometimes an ear infection leaves fluid in the middle ear area that could develop into symptoms after the infection. Ear fluid can accumulate because of a cold or an allergy attack, resulting in blockage of the eustachian tube extending from the middle ear to the throat area. Due to the blockage, fluid might not flow out of the middle ear. Sometimes the eustachian tube obstruction could be because of enlargement of the adenoids situated around the eustachian tube opening.

Being subject to a change in atmospheric pressure, as can happen during an airplane ride, can affect the eustachian tube. This could lead to acute serous otitis media symptoms. In rare instances, the presence of a tumor or growth in the eustachian tube may be an underlying factor in the condition in adults.
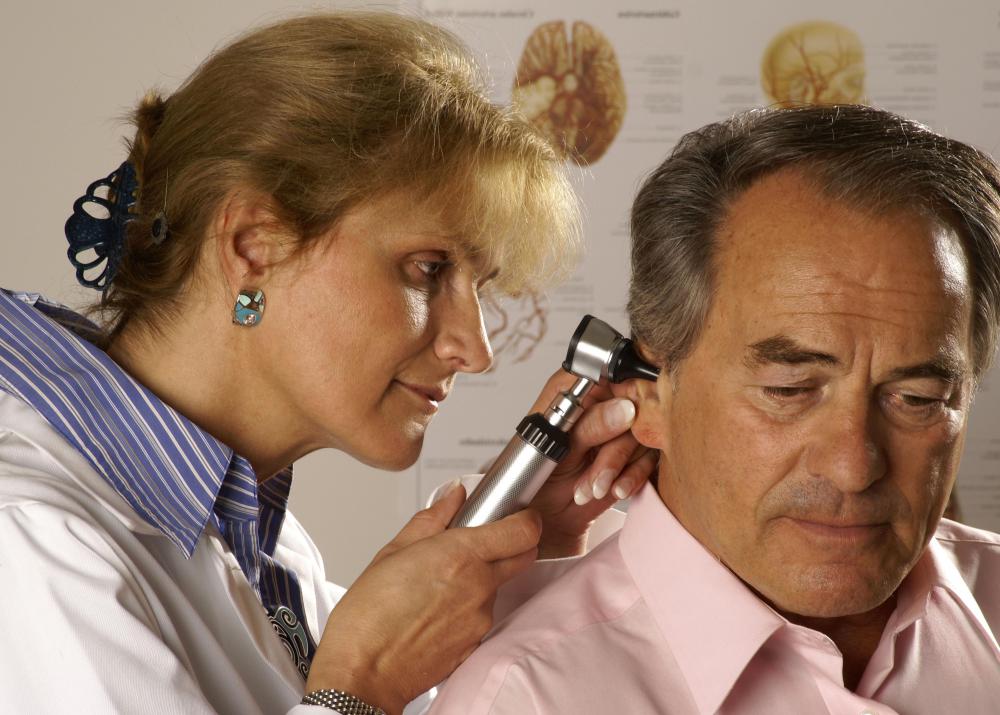
To diagnose serous otitis media, a doctor usually examines the eardrum, which is a part of the middle ear. Air may be squeezed into the ear to check eardrum movement. Sometimes a simple test known as tympanometry, which involves the use of a device with a microphone and a sound source, might be conducted. This test assesses fluid accumulation behind the eardrum and the functionality of the eustachian tube.

Normally, accumulated ear fluid may clear up within a few weeks after a cold or an ear infection subsides. If the condition continues, a doctor could prescribe a course of medication that includes antibiotics. Surgery to put in drainage tubes might be advised if symptoms are not relieved even after three months or if an ear infection occurs often. Generally, a specialist in ear, nose, and throat disorders can evaluate a patient and prescribe suitable treatment for serous otitis media.
A myringotomy is one of the surgical techniques that could be used to treat the condition. This procedure customarily involves putting a tiny tube in the eardrum of the affected ear to drain the fluid and let air reach the middle ear area to relieve pressure. The tube usually remains in the ear for six to 12 months and drops off thereafter. In a few instances, a doctor might recommend surgery to excise the enlarged adenoids, therefore helping the eustachian tube to function better.
The incidence of the condition could be reduced by taking certain precautions. These include minimizing exposure to factors that trigger allergy attacks. Another measure is to possibly avoid an airplane journey when one has a cold. Breastfeeding often lowers the likelihood of ear infections in childhood. Enrolling a child in a daycare with a smaller group of children can help prevent recurring ear infections and consequently ear fluid disorders, as well.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
My young son got serous otitis media last year, and he almost had to have surgery to repair his inner ear tube. The doctor prescribed a strong antibiotic, and suggested warm compresses to help ease the pain of the fluid in his ear. My son got better in about three weeks, but he told me he thought he was going to be permanently deaf in that ear at one point.
I once contracted serous otitis media as an adult, and I suspect I got it from being around younger relatives at a family reunion. A few days after the event, I felt a little fluid building up in my ear. The next morning, the ear felt completely blocked and the pressure was painful. By the time I got to the emergency room that night, I was almost completely deaf in that ear.
The doctor examined my ear and diagnosed me with otitis media serous. He told me he usually didn't see this kind of ear infection in adults, but it could be transmitted from an infected child. He prescribed a round of antibiotics and sent me home. I ended up having to have two more rounds of antibiotics before the swelling subsided and I got my hearing back in that ear.
Post your comments