At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Diagnostic Cytology?
Cytology generally refers to the study of cells found in living things. Diagnostic cytology is the process of studying cells to identify diseases. Procedures to obtain cell samples to perform cytological evaluations are varied, but usually involve taking either a sample of body fluids or a scraping of cells from body tissue. Diagnostic cytology may be used to help identify various types of cancer and certain infections.
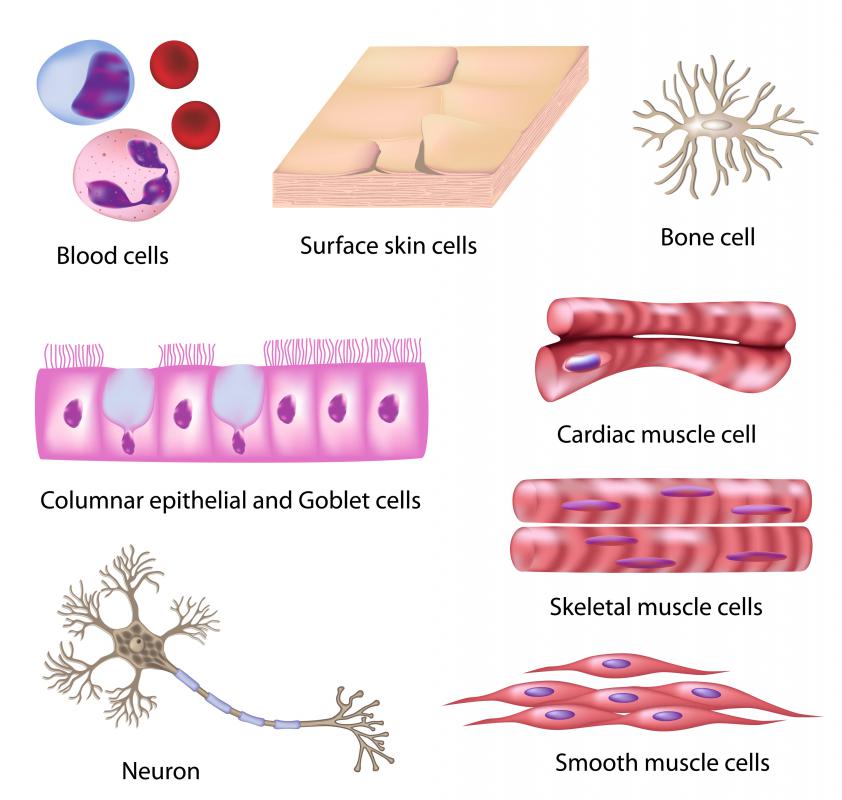
The human body is made up of many different types of cells, from immune system and blood cells found throughout the body to specialized cells found only in certain organs. When viewed under a microscope, all types of cells have certain physical characteristics that differentiate them from other types. Certain diseases and infections can affect how cells function and look, or where they are present in the body. Diagnostic cytology can help pick up on these changes and determine what disease is causing them.

There are several different procedures that can be used to obtain a sample of cells from the body for diagnostic cytology testing. The method typically depends on the area being studied. For example, if a health-care provider suspects a problem in the bladder or urinary tract, a urine sample may be taken for further testing. If a problem is suspected in tissue that can be accessed relatively easily, such as the mouth or cervix, a scraping of cells may be taken directly from the tissue this area.

Cervical cells are one of the common subjects of diagnostic cytology. A scraping of cervical cells, commonly known as a pap smear, is frequently done to screen for cervical cancer. This same test may also diagnose certain infections, such human papillomavirus. In general, cells scraped from the surface of the cervix in a pap smear are mounted onto a slide and dyed with a special chemical so they can be easily seen under a microscope. A diagnostic cytologist typically then evaluates this prepared sample to see if the cells present are normal or show changes that could be indicative of cancer or infection.

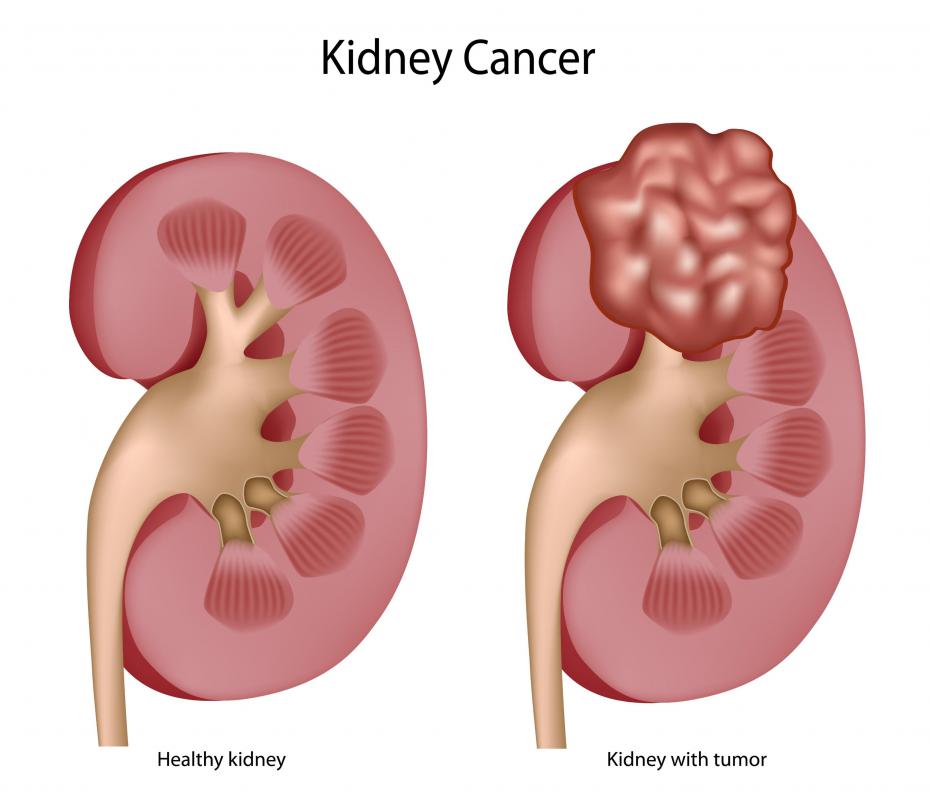
Other types of cancer and infections may also be diagnosed via diagnostic cytology. For example, bladder and kidney cancer may be diagnosed by the evaluation of cells obtained from a urine sample. An infection known as bacterial meningitis may be found by cytological evaluation of cerebral spinal fluid. In some cases, diagnostic cytology can only identify that something is not normal. Other types of testing, such as DNA tests or tissue biopsies, may be needed to confirm the actual disease or infection.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
@Ana1234 - I don't think anyone just sits and looks at microscope slides all day. They all do a range of different laboratory testing.
I know I might be singing a different song if it happened to me, but I accept that there are sometimes mistakes made. I had a friend who was misdiagnosed multiple times before they finally sent back the result that we had all been waiting for (it wasn't anything fatal) and she could finally go on the proper medication.
It's not a perfect system, because the human body isn't perfect, but it's better than anything we've had in the past and I'm thankful for these kinds of systems, perfect or not.
@croydon - That's exactly why I wouldn't want to be stuck in a diagnostic cytology lab. There are so many misdiagnoses every year and in some cases, it can lead to the person completely ruining their life (in the case of people who are misdiagnosed positive) or even losing their lives (in the case of people who were misdiagnosed negative).
I just would not like that kind of pressure around a task that seems like it would quickly become routine. I mean, I appreciate being able to marvel at stuff under a microscope, but the wonder wouldn't last long. Eventually it would become ordinary and, since you'd be diagnosing the same stuff over and over, it would even be boring. And when someone feels bored, that's when mistakes are made.
I really enjoyed using a microscope when I did my units in science at university. There's an element of wonder in seeing what makes up the world.
And cells are so complex and interesting. I could definitely see why someone would go into this kind of profession and work on clinical cytology. As a bonus, you'd also be helping people to identify their disease and perhaps saving their lives.
Post your comments