At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Ataxia?
Ataxia comes from the Greek a taxia, meaning literally "no order." It is a blanket term referring to a loss of ability to control one's muscles. There are a number of causes and treatments for it.
The condition can be broken into two distinct groups: sporadic and hereditary. Hereditary ataxia can usually be traced to a family history, and can be linked to twenty-two gene mutations. These mutations are labeled "spinocerebellar ataxia type 1" through 22 — in shorthand referred to simply as SCA1-22. Sporadic ataxia is a form that is not linked to a genetic defect.

Hereditary ataxia can be separated into types caused by a metabolic defect, and those which fit the mold of a named disorder. In all cases they are inherited from a defective gene, and the identification of these genes continues at an encouraging pace. Some of the many types include Machado-Joseph disease, ataxia with opthalmoplegia, spinopontine atrophy, ataxia with etinopathy, and slow-eye movement ataxia.

The sporadic type is very difficult to diagnose, and often doctors will struggle as they rule out every hereditary possibility before making a final diagnosis. Some of the many terms used to describe sporadic ataxia are spastic ataxia, Menzel's ataxia, Marie's ataxia, Holmes' ataxia, sporadic atrophy, and most commonly sporadic OPCA, or sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy.

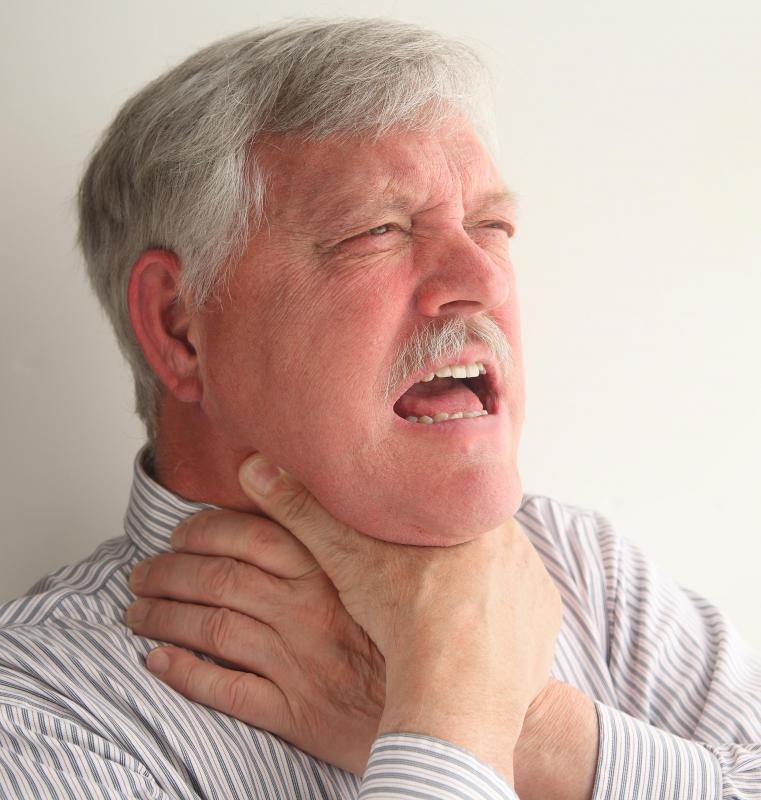
Diagnosis is usually based on observing neurological symptoms and, where applicable, existence of other affected family members. Common symptoms which may be caused this condition include choking (dysphagia), an incoordination of extremities, slurred speech (dysarthria), and a stiffness of movement. Most physicians will first attempt to rule out other causes for these symptoms, such as a recent stroke or multiple sclerosis, before making a final diagnosis.

After an initial diagnosis, a patient should immediately consult a neurology specialist for a second diagnosis, after ruling out all alternative neurological causes. Ataxia is at present incurable, and so the task facing most people who are diagnosed is one of learning to adjust their lives to coping. Finding qualified live-in aides is an important first step, as is pursuing physical and speech therapies, and finding a support community to learn to live with the new disease.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments