At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Thiamine Injection?
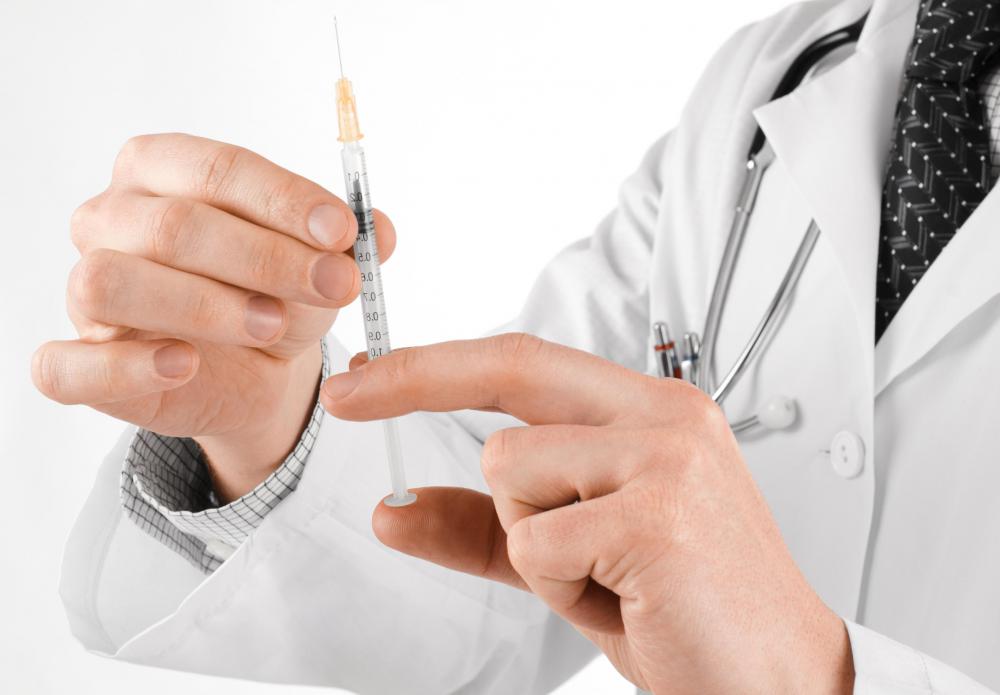
A thiamine injection is a method of administering vitamin B1. Thiamine is available in oral supplements, but an injection may be prescribed when an oral method would be insufficient or inappropriate for treatment. It is injected into a vein or muscle, and redness, swelling, or discomfort may occur at the site of injection; other side effects include sweating, weakness, and nausea. A thiamine injection is relatively safe, but if there is any suspicion of an overdose, a person should contact an emergency room or poison control center immediately. Allergies to vitamin B1 are rare, but any patient with a known allergy to vitamins in the B complex should notify their doctor before using a thiamine injection.
The frequency and dosage of the injections is left to the prescribing doctor's discretion, but a typical patient may expect to perform a thiamine injection three times per day. A daily recommended dosage in the United States (US) for teenagers and adults can range between .8 mg and 1.5 mg, depending on the gender, age, and weight of the patient. Different countries have varying recommendations for maximum daily dosage.

Non-human animals can have thiamine deficiencies, and injections are generally the preferred method of treatment. Dosages for large animals, such as cows, can be as large as 1,000 mg over a two-day period. Appropriate treatment for an animal typically should be determined by a veterinarian.
Vitamin B1 is readily available in many food sources, so a human eating a healthy diet will not typically require any thiamine supplements. There are, however, conditions that increase the body's need for vitamin B1. Patients suffering from liver disease, burns, alcoholism, or continuous stress may have a thiamine deficiency. Many diseases and procedures that inhibit gastrointestinal functions can result in thiamine deficiencies.

Insufficient thiamine can develop into serious conditions, such as Beriberi or Wernicke's encephalopathy. The causes of vitamin B1 deficiencies are numerous, but the deficiency itself is easily diagnosed with a blood test. Many times, these dangers can be predicted and thiamine can be prescribed in advance.
Thiamine is soluble in water and may require mixing at home. It is important for a person to follow both the prescribing physician's instructions and any directions on the vitamin's label or packaging. If in doubt, a person should call a physician for clarification. Generally, thiamine should be stored at room temperature, away from light and heat sources. Any needles or syringes used for injection should be immediately discarded in a hard container, and a clean needle should be used for every injection.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
I remember when my mom was a young mother, she had a iron deficiency due to anemia. She had to go to the doctor several times a week for shots. I don't think they had any self-injections in those days.
Then the doctor told her she needed to eat big juicy steaks a couple of times a week to enrich her blood with iron. She and my dad enjoyed following those doctor's orders.
Anyway, it wasn't too long before she was feeling a lot better and the anemia was gone. It must have been the steaks!
Most people in the United States should get enough vitamin B1 or thiamine by just eating an adequate diet, including some meat and eggs and milk. But it seems like diseases, like liver disease, excess stress, severe burns and alcoholism can cause a deficiency in thiamine.
It's probably fairly common in some third world countries where meat, eggs and milk are not available for everyone.
Since those who are highly deficient need to have thiamin B1 injection solution for at home use, they need to learn how to mix the solution and give it to themselves three times a day. I think that would be a hard thing to do to yourself.
Post your comments