At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is a Marfan Syndrome Test?
A Marfan syndrome test is used to diagnose whether a person has this condition. Imaging tests such as an echocardiogram or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done to examine the aorta. Genetic testing will determine if there are changes on the FBN1 gene usually associated with Marfan syndrome. There are a few other types of Marfan syndrome tests performed along with imaging, such as tests on the eye and bone structure.
Marfan syndrome affects the connective tissue in the body. The condition impacts many areas of the body, including the heart, eyes, and bones. Usually, the condition is inherited and occurs due to a malformation of the FBN1 gene, which is responsible for the body's connective tissue. Signs and symptoms of the condition may be so mild as to be barely noticeable.

Typically, more than one Marfan syndrome test needs to be performed on a patient to make a diagnosis. An echocardiogram is usually the first Marfan syndrome test. The test is an ultrasound of the heart and aorta. During the test, the size of the aorta will be noted, as a common symptom in Marfan syndrome is an enlarged and weak aorta.
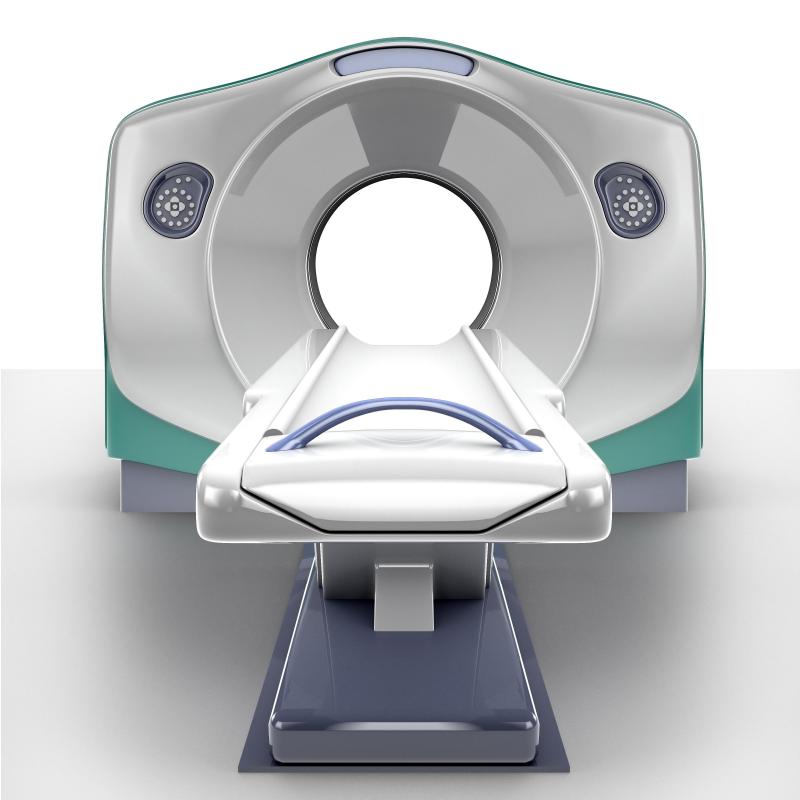
Other imaging tests include an MRI, which helps a doctor look at the size and shape of the aorta. An MRI also lets a doctor see the spinal column and look for dural ectasia, or bulging in the spine, which is a common indicator of Marfan syndrome. A computerized tomography (CT) scan can also be performed to let the doctor see the aorta. MRI or CT scans may be needed if the echocardiogram does not show the aorta clearly.

As the condition also affects the eyes, another Marfan syndrome test is the slit-lamp examination. A doctor uses this test to find out if a patient's lens or retina is detached. During the procedure, the doctor puts drops in a patient's eyes to dilate the pupils so that the doctor can look into the eyes using a microscrope known as a slit lamp.
Other common tests include looking at the bone structure of a patient. A doctor will measure the patient's skeleton and her arm span to help diagnose the condition. Usually, patients with Marfan syndrome have a very wide arm span.
A genetic test is available to determine if a patient has Marfan syndrome as well. The test is usually done only if a diagnosis cannot be made using the other tests. A sample of blood is taken and examined for changes on the FBN1 gene. Typically, genetic tests are more expensive than the other options, but they may be useful, especially if a person in the family has been diagnosed with Marfan syndrome.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:











Discuss this Article
Post your comments