At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Malignant Schwannoma?
Schwann cells are cells in the nervous system that produce the myelin sheaths covering peripheral nerves. A Schwannoma is a tumor made up of Schwann cells that wraps itself around a neuron. A malignant Schwannoma, or a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, is a cancerous type of Schwannoma. Schwannomas consist solely of Schwann cells and are relatively slow to grow. Although Schwannomas always develop outside of a nerve, they may put pressure on the nerve or surrounding tissue.
Schwann cells are glial cells, one of the types of cells that make up the nervous system. Glial cells are support cells, which help keep neurons up and running. Schwann cells wrap themselves around neurons to form a fatty myelin sheath, which insulates the neurons and speeds up their signaling. They are also involved in nerve development and regeneration.

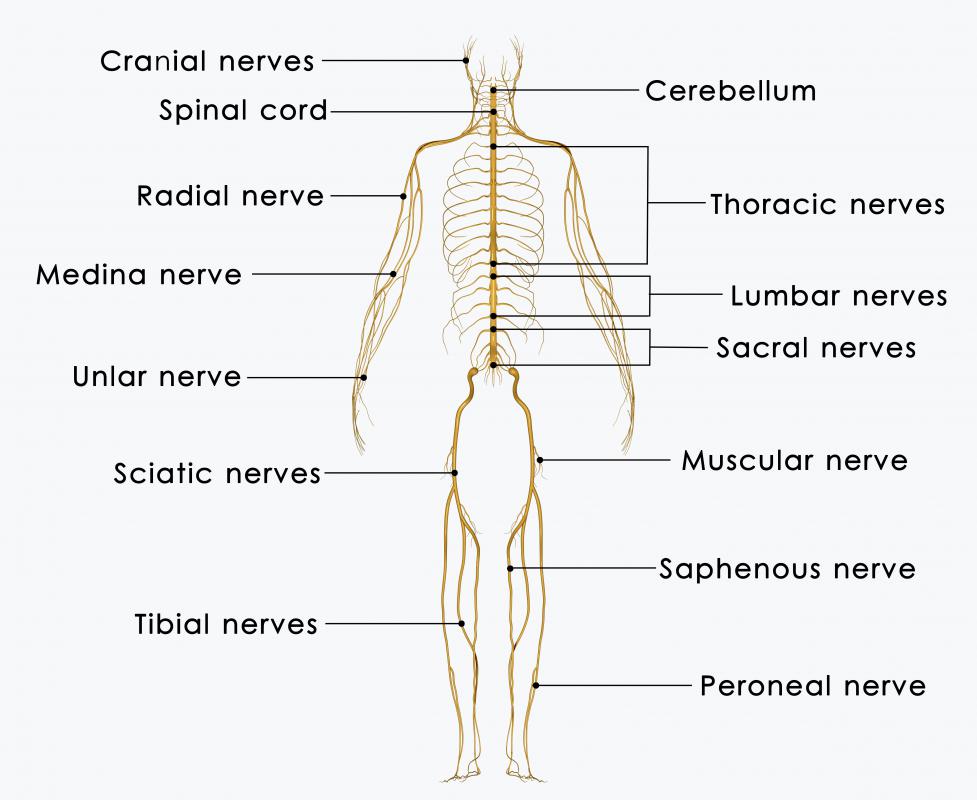
A malignant Schwannoma is a type of soft tissue sarcoma. It often affects the sciatic nerve, the nerve that begins in the lower back and runs through the leg. These tumors can also be found at the brachial plexus, or nerves at the top of the arm, and the sacral plexus, a bundle of nerves in the lower back. The most common type of Schwannoma is called acoustic neuroma, because it grows on the eighth cranial nerve, which controls hearing. An acoustic neuroma can cause deafness.

Most Schwannomas are benign, and only about 1 % become malignant. A malignant Schwannoma develops into a form of cancer called neurofibrosarcoma. This form of cancer is dangerous, however, it is not often lethal. A study at Massachusetts General Hospital found an 85 % survival rate among patients with a malignant Schwannoma.
About half of all cases of malignant Schwannoma occur in people with neurofibromatosis, a genetic condition that affects nerve cells. The severity of neurofibromatosis can vary from person to person. The tumors that grow as a result of this condition can be either benign or malignant. Even the benign tumors may be problematic, however, because they can compress nerves and tissues.

A malignant Schwannoma is typically treated with surgery to entirely remove the tumor. This surgery is not always effective, however, and the tumor may grow back. Radiotherapy, a technique where high energy waves are directed at a tumor, may help prevent a malignant tumor from growing back. It can also be used to slow the growth of cancerous tumors or even shrink them. Chemotherapy is another treatment, however, it is not as commonly used for soft tissue sarcomas like malignant Schwannomas.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:

















Discuss this Article
Post your comments