At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Humerus?
The humerus is the first and largest long bone of the frontal, or upper, limb. This bone connects to the body at the shoulder joint, and articulates distally with the radius and ulna at the elbow joint. An evolutionary adaptation to assist in locomotion, the humerus is present in most of the broad group of animals classified as tetrapods, or four-footed animals. This group includes reptiles, amphibians, birds, and mammals.
Among primates and certain other animals, the humerus is primarily used not for walking, but for climbing and assisting in object manipulation. The upper arm bone provides attachment points and support for the muscles of the chest, upper back, shoulders, and arms. Working with these muscles, it allows arm movement along multiple planes of motion, making it one of the most free-moving bones in the human body.

First seen in the early Devonian period, some 400 million years ago, the humerus made its initial appearance among fish-like tetrapods. These early forelimbs were too club-like and clumsy to have been used in walking, and were most likely employed in navigating underwater obstacles and currents. As time went on, these stubby appendages were replaced by sturdy, fully formed limbs that would have allowed early tetrapods to travel between diminished water bodies during dry periods.

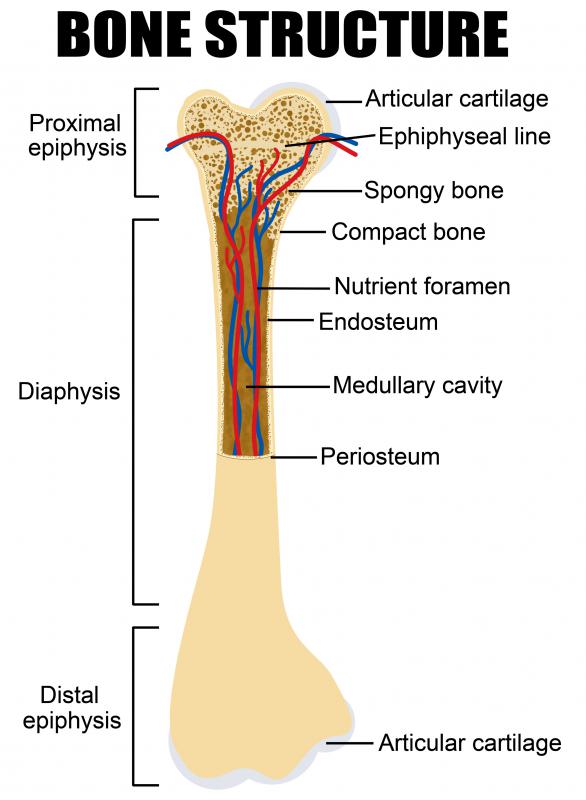
Most modern versions of the humerus have elongated somewhat, but otherwise changed little from the early form. Structurally, the humerus consists of a long, cylindrical center termed the diaphysis, with enlarged ends known as epiphyses. The epiphysis that fits into the socket joint at the shoulder has a ball shape, and is generally termed the humeral head. The lower epiphysis, known as the condyle, has a variety of structures to facilitate the movement of the articulating bones and tendons of the forearm.

In children and adolescents, there is a zone of rapid cell division between the diphysis and the epiphysis known as the epiphyseal plate, or growth plate. This is a region of rapid cell division where elongation of the bone takes place during periods of growth. The growth plate is vulnerable to trauma and is a common fracture site among children. Once growth is completed, this zone ceases its characteristic acceleration of cell division, and is termed the epiphyseal line.

The humerus is similar to other long bones in composition and structure. The exterior surface is rough and irregular, containing multiple epicondyles, processes, and fossae to facilitate the attachment of muscles and tendons. Like other bones, it has both an outer and an inner layer of connective tissue. The outer layer, known as the periosteum, contains fibroblasts and nerve endings, making it very sensitive to injury or manipulation. This layer of connective tissue is responsible for the generation of new cells during bone growth or healing.

Beneath the periosteum lies the endosteum. The endosteum is a tough, fibrous membrane that surrounds the bone tissue itself. Within the bone, the spongy tissue is impregnated with bone marrow, where bone, lymph, and blood cells are manufactured. A network of interconnecting canals run through the bone and act as channels for blood vessels carrying oxygen and nutrients.

Fractures of the upper arm are classified as proximal, mid-shaft, or distal. Proximal fractures occur at or close to the shoulder joint, and may involve muscles of the rotator cuff. Mid-shaft fractures typically happen along the long portion of the bone, and are most likely to involve the radial nerve, which services much of the arm itself. Distal fractures take place near the shoulder joint and are rare among adults. Humeral fractures are often treated with a sling or brace, and all but the most severe will usually heal well without surgery.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
The "funny bone" got its nickname because of that funny feeling you get after you hit it, but your funny bone isn't actually a bone. It is the ulnar nerve that runs down the side of your elbow and lets your brain know about feelings in your fourth and fifth fingers. It's also one of the nerves that controls some movement of your hand.
You get that funny feeling when the ulnar nerve is bumped against the humerus. Tapping your funny bone doesn't do any damage to your elbow, arm, or ulnar nerve.
Is the humerus also known as the "funny bone"?
Post your comments