At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is a Coagulation Pathway?
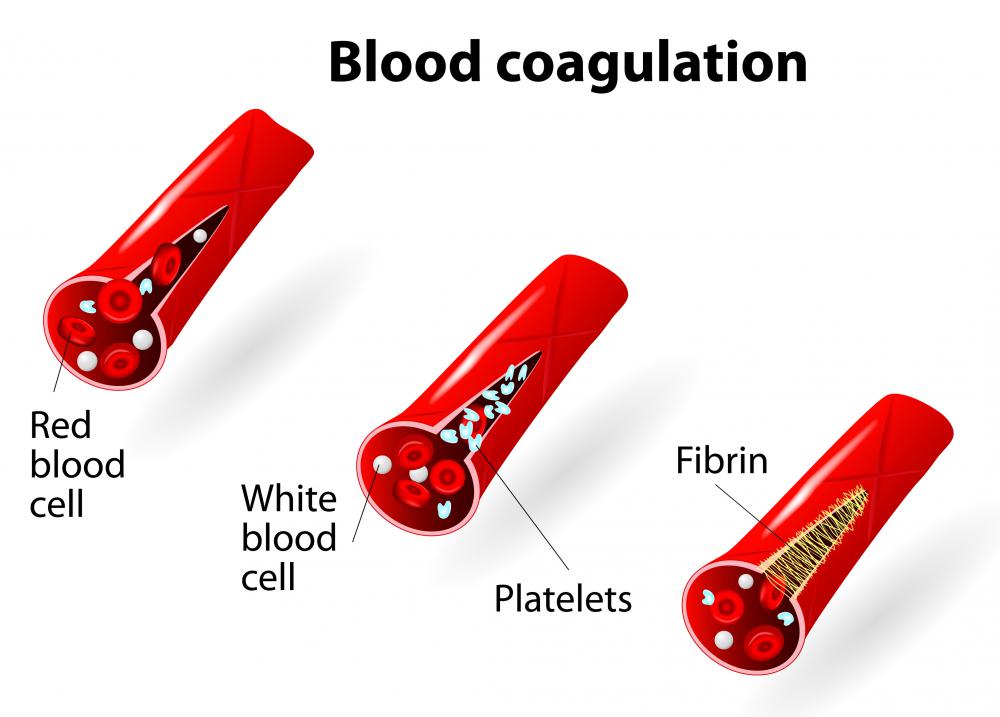
The purpose of the body’s blood vessel coagulation pathways is to give the opportunity and means to the body for repairing itself after injuries. After punctures, these blood vessel pathways can seal off blood loss and provide surface wounds with anti-inflammatory assistance from exposure to viruses, bacteria, and fungi that might seep into the wound. There are two main coagulation pathways, known as the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathways. Normal functioning in these pathways helps to keep a healthy balance of coagulation growth factors in the body’s organs. Bleeding triggers blood platelets, factors, fibrin, and proteins that in sequential activations of each other form the protective barrier known as a clot.
The intrinsic coagulation pathway, sometimes called the contact activation pathway, is triggered by encountering a foreign substance such as plaque in the blood. This creates an inflammation response and forms collagen. Collagen activates other blood substances and a clotting factor known as factor X, causing the intrinsic pathway to converge with the extrinsic coagulation pathway. The extrinsic coagulation pathway is usually involved when tissue from outer layers of the skin comes into contact with blood through a break in a blood vessel. Tissue factors together with other clotting factors in the blood start to bind with platelets drawn to the event, and together they form a semisolid clot from a substance known as fibrin, which becomes a hardened clot.

Clotting medications known as procoagulants imitate the pathways’ clotting functions to help the body to clot when necessary. Medications that fight the body’s ability to clot when the body tends to clot too easily are known as anticoagulants. The use of procoagulants and anticoagulants treat disorders when they occur in the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Procoagulants are used for treating excessive bleeding from deep puncture wounds, for example, and thrombin and fibrin from the pathways are combined to form a glue patch that is sometimes used to seal off blood vessel ruptures called aneurysms.

Serious diseases occur from disturbances within the coagulation pathway. Some of these diseases are those of patients with not enough clotting capability, as in hemophilia and hemorrhage. Those patients with too much clotting ability often suffer from different forms of thrombosis. Thrombosis, when the body clots too well, forms traveling clots that lodge in the circulation of the lungs, brain, and heart, and can cause death.

Secondary diseases also can come about from disturbances of normal coagulation pathway function, such as lupus and some forms of cancer. Liver failure can occur due to insufficient coagulation ability in the liver. Sepsis patients have a disorder of the fibrinolysis functioning found in the coagulation pathway, which can lead to a condition known as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), due to a very dangerous procoagulant imbalance.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discuss this Article
Post your comments