At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Canaliculus?
A canaliculus is any one of the minute tubes or canals that funnel through various areas of the body. These narrow passageways can carry nerves, veins, or capillaries, but in most cases act as conduits for bodily fluids. The term is rarely used by itself, but rather as part of a more specific anatomical term in terms of medical studies and reports. Most often, the terms "ducts" or "canals" are used instead.
The most prominent canaliculi are those in the bones, which spread out like spokes in a honeycomb pattern, connecting the lacunae. Lacunae are the microscopic tubes which carry osteocytes, nutrients, and waste to and from the bone in the same way blood vessels transfer nutrients and waste through the body. A bone canaliculus acts as a gutter for periosteocytic fluid, which is made up of materials too large to be filtered through thick bone tissue, such as calcium and phosphate ions.

The lacrimal canaliculi are likely the most commonly recognized of any canaliculus, though most people know them by their more common name — tear ducts. This canaliculus connects the lacrimal lake to the lacrimal sac. Put more simply, the canal is the dispenser chute for tears, constantly refilling the lacrimal sac as tears are released.
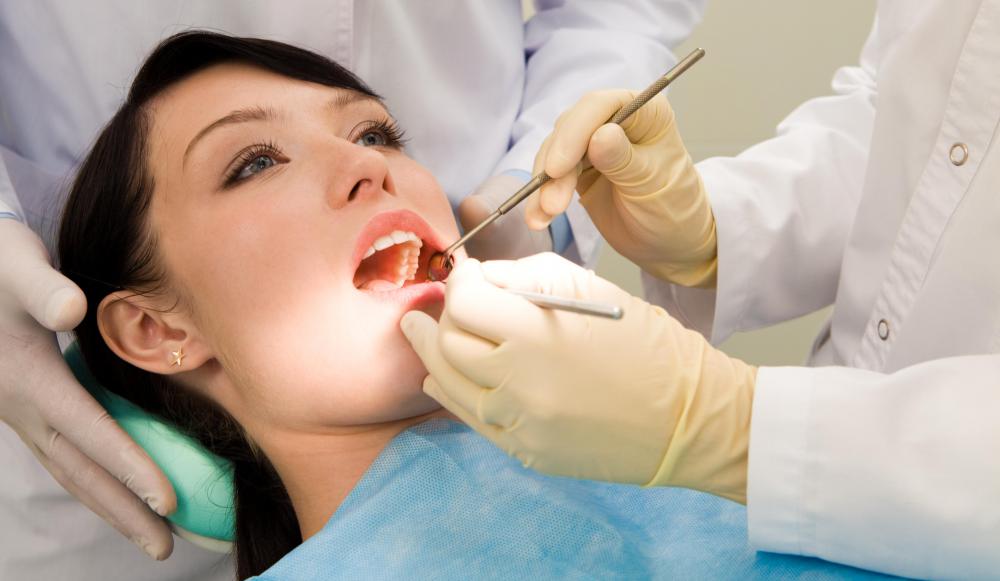
Dental canaliculi are the veins of the teeth, which carry blood and nutrients from the pulp at the base of the tooth to the enamel. At their roots, these canaliculi are dense and tightly bunched. They diminish in both size and proximity as they extend closer to the enamel.

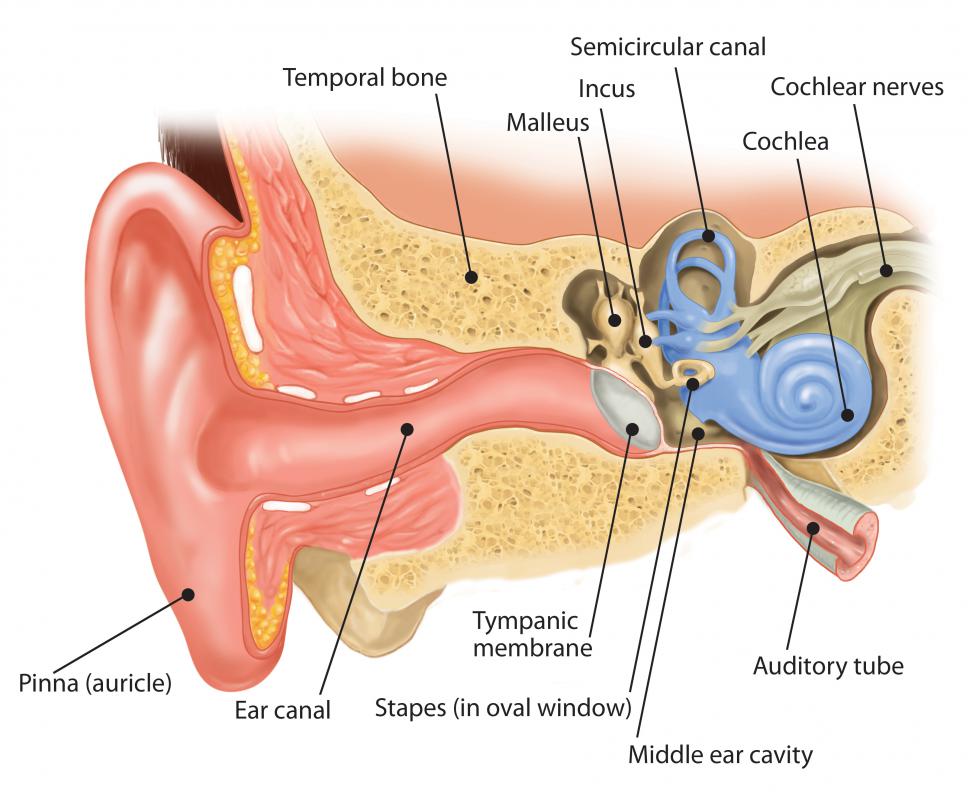
A cochlear canaliculus is housed in the temporal bone of the ear, and acts as a housing for the smaller perilymphatic duct. The perilymphatic duct aids in draining any excess perilymphatic fluid that may build up in the ears. Also in the temporal bone is the mastoid canaliculus, which carries the auricular branch of the vagus nerve, or what is essentially the speaker wire between the ear and the brain. The mastoid canaliculus is near, but not connected to, the tympanic canaliculus, which houses part of the glossopharyngeal nerve and a main artery to the ear cavity.

Other types of canaliculi are the apical canaliculus, which connects the kidney to the apical cytoplasm, and intercellular and intracellular canaliculi. These two connect the parietal cells which generate the hydrochloric acid to aid digestion. Slightly south of those are the bile canaliculi, which together form the bile ductiles.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:











Discuss this Article
Post your comments