At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are Granulosa Cells?
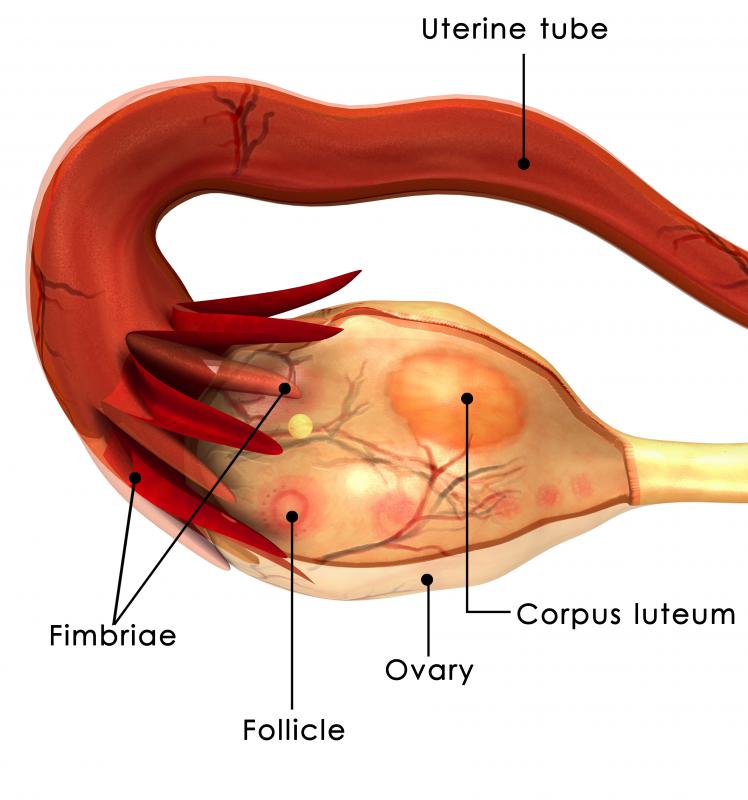
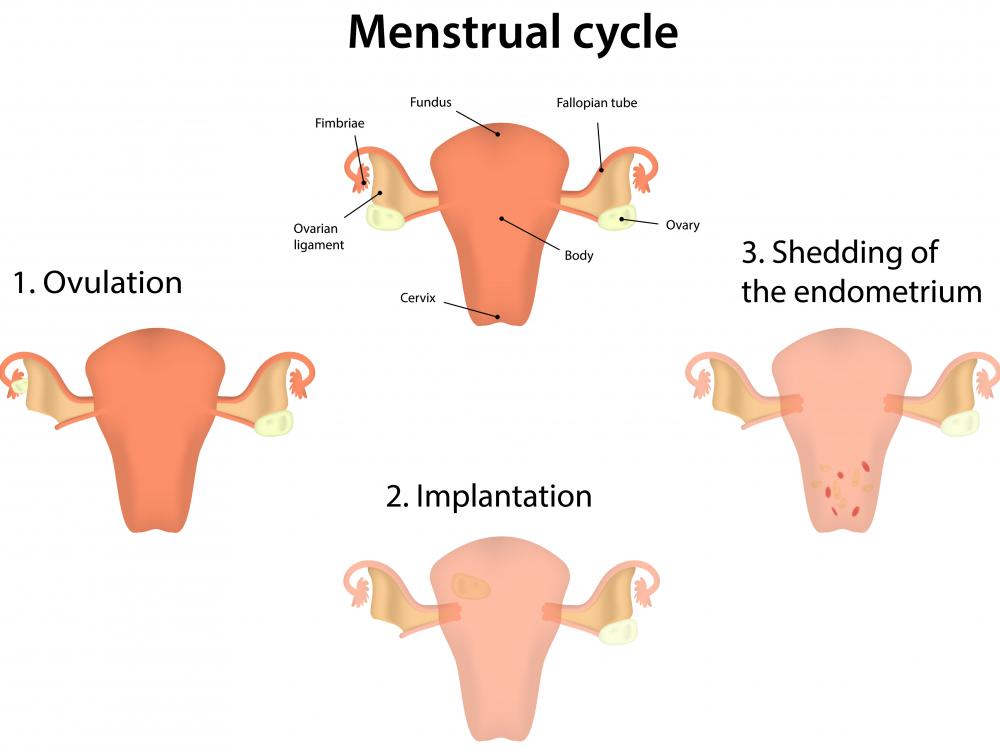
Granulosa cells are cuboidal cells that form a barrier around developing oocyte follicles within the ovary. As the follicles mature, the granulosa cells multiply to form many layers around the oocyte. Before ovulation, the cells manufacture estrogen, which is then secreted into the bloodstream. After ovulation occurs, these cells become granulosa lutein cells and primarily produce progesterone. The progesterone keeps the uterus ready to implant an egg, and sustains a pregnancy if fertilization occurs.
The granulosa cells form a capsule called the cumulus oophorus that protects only one developing oocyte at a time. Many oocytes begin the maturation process at the beginning of the menstruation cycle, but normally only one will complete the process. The follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) signals the oocyte to begin the primary follicle stage. Oocytes at this stage have only a single layer of these cells surrounding them.

When the granulosa cells form a many-layered boundary around the oocyte, this is referred to as the secondary follicle stage. The cells outside the follicle separate into theca interna and theca externa cells before the oocyte proceeds onto the tertiary stage, also called the Graafian follicle. Soon after reaching the tertiary stage, the follicle will rupture, releasing the oocyte to travel through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. The oocyte at this stage will have an attached layer of granulosa cells called a corona radiata.

Leftover granulosa cells of the ruptured follicle form the corpus luteum. This structure secretes the progesterone necessary to maintain a pregnancy until after the first trimester. If there is no pregnancy, the corpus luteum will degrade into a small fibrous scar called a corpus albicans.
The primary purpose of the granulosa cells is to provide nutrients to the maturing oocyte. Sometimes a tumor may form out of granulosa cells. These tumors are most often seen in the ovaries of women, although granulosa tumors in testicles have been reported. After testing, most tumors are found to be benign. Rarely, a benign tumor, called a juvenile granulosa cell tumor, may form in children that have not reached puberty.

Granulosa cell tumors are smooth and rounded in appearance. Internally, the tumors contain cysts that can fill with blood. The tumors cause changes in the estrogen levels, detectable throughout the body. Surgical removal of the tumor is the most likely course of treatment. After the surgery, the estrogen in the body returns to normal levels. The cause of these tumors is unknown.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments