At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are Fibroid Tumors?
Fibroid tumors are tumors which develop in areas of the body with smooth muscle cells. The vast majority of fibroids, as these tumors are sometimes called, appear in the uterus, most classically in women between 30 and 40 years of age. Fibroids are also sometimes referred to as leiomyomas or myomas. Treatment for fibroid tumors depends on the woman and her individual symptoms, although because these tumors are benign and typically slow-growing, often the best treatment is just to leave the fibroids alone.
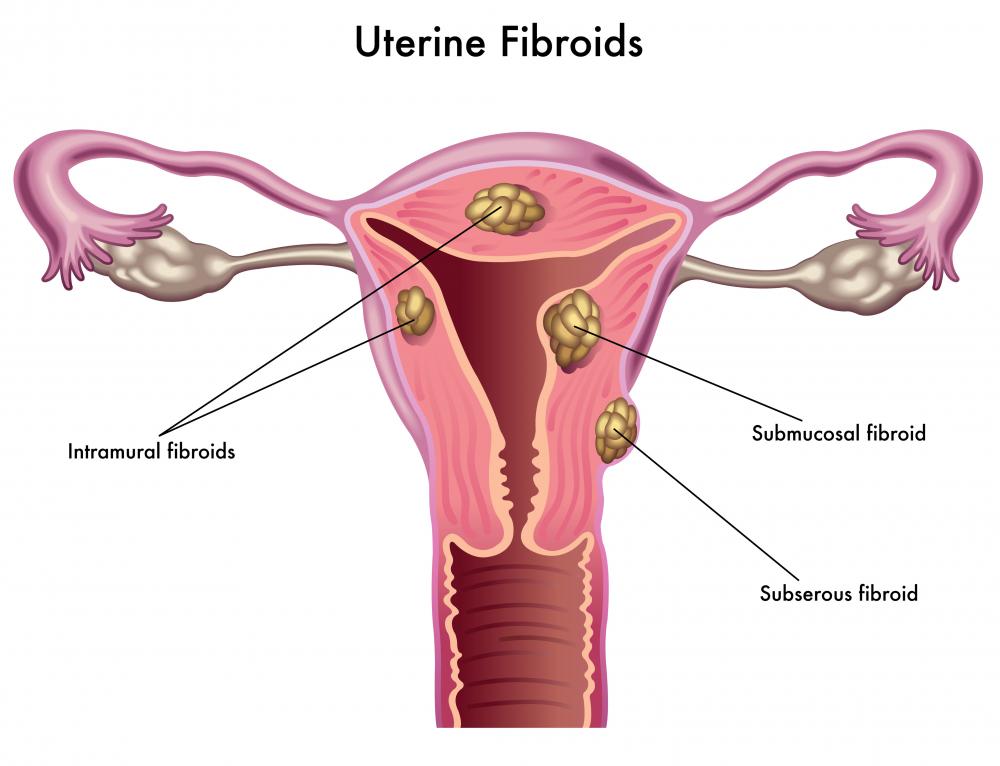
As the “fibroid” suggests, fibroid tumors are comprised of fibrous material which makes them hard to the touch. They can grow inside the muscle walls of the uterus, in which case they are known as intramural tumors, or they can start just below the mucosa which lines the uterus, developing into submucous fibroids. If these tumors start near the outside wall of the uterus, they are called subserous fibroids, and these tumors can also develop on small stalks inside the uterus, becoming pedunculated tumors.

The cause of fibroid tumors is not known, but tumor growth appears to be directly linked with estrogen levels. These tumors do not appear in girls who have not yet reached puberty, and they tend to shrink in older women after menopause. During pregnancy, when estrogen levels are highly elevated, these tumors can grow at a very rapid rate.
Many women experience no symptoms, and find out about fibroids during a routine gynecological exam. In other cases, women experience breakthrough bleeding, menstrual cramps, or swollen abdomens, in the case of large fibroids. Some fibroids, an estimated seven to 13%, have been linked with infertility. In extremely large cases, fibroid tumors can cause difficulty urinating, constipation, and backache, suggesting a need for treatment to relieve these symptoms.

There are a number of treatment options. In a myomectomy, these tumors are simply removed. However, they often recur after this procedure, and this procedure also creates a risk of surgical adhesions, which can cause pain later on. A hysterectomy may be used in extreme cases, especially if a woman has no plans to have children, and some doctors can perform a procedure which reduces bloodflow to the fibroids, which will cause them to shrink.

The best treatment option for the tumors varies, depending on the number of fibroids a woman has, how large they are, which symptoms they are causing, and a woman's plans for children. Treatment options should be discussed with a gynecologist to decide on the best course of action.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
Some women with fibroid tumors have no symptoms at all, but in more serious cases, women report heavy menstrual periods, periods that last longer than seven days, a feeling of pressure in the abdomen, difficulty urinating and constipation. The prolonged periods can also cause anemia, which has symptoms of its own. People with anemia might feel tired or short of breath.
Post your comments