At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are Collagen Supplements?
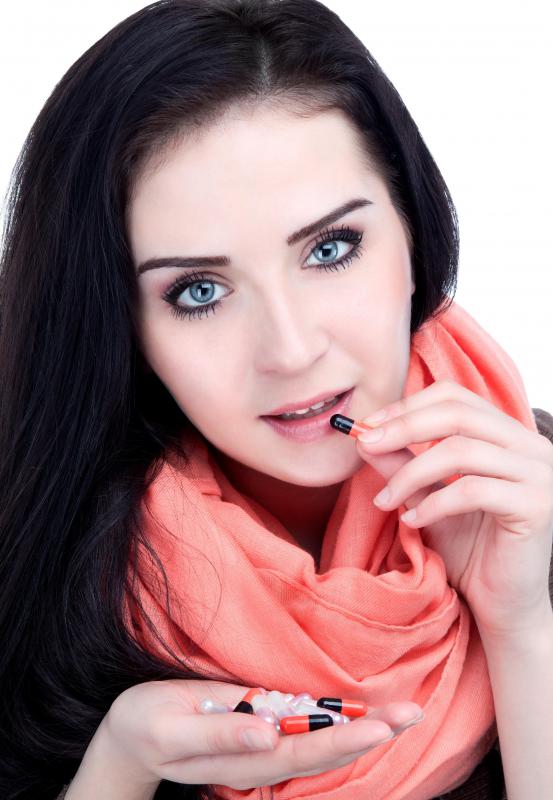
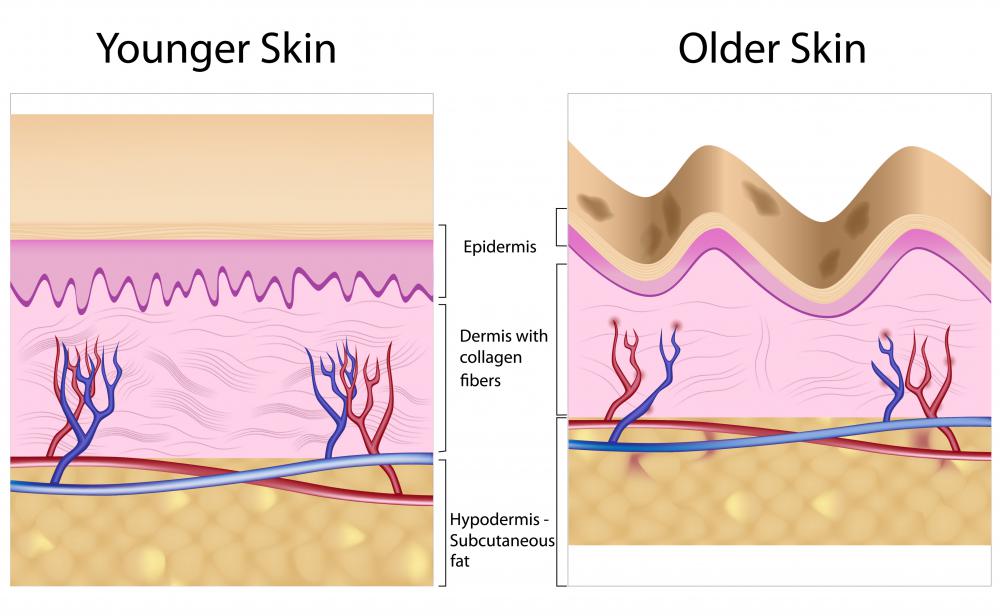
Collagen supplements are dietary supplements, usually in capsule form, taken to reduce the symptoms of arthritis and bone pain, to promote healing, or to improve the appearance of the skin. Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, including humans, and makes up the bulk of the connective tissue, including the skin, bone, teeth, tendons, cartilage, and organs. It supports the softer tissues of the body and aids in healing. Healthy people generally do not need to take collagen supplements, but many people choose to take them to manage bone and joint pain, or to promote a youthful appearance.
There are many different types of supplements containing collagen, and the kind one should use depends on his or her reasons for taking it. For arthritis or orthopedic injuries, those with glucosamine are often the best choice. Like collagen, glucosamine aids in joint healing, and can improve motility and reduce pain. Supplements containing collagen II, rather than collagen I or III, are most often indicated for patients with arthritis. Collagen II is the main component of hyaline cartilage, which lines the ends of bones to form the surface of joints.

A person taking collagen supplements to improve the look of the skin, nails, and hair should opt for formulas without glucosamine. There is no need to take glucosamine if not concerned about joint health, and supplements with glucosamine are more expensive than those without. Non-glucosamine supplements often contain collagen I and collagen III, which are most abundant in the skin.

Collagen supplements come in different dosages. When used as a beauty supplement, collagen should be limited to about five or six grams daily, while more may be required to address joint or bone pain. Arthritis patients may take up to 10 grams of collagen daily. Collagen is water soluble, so excess amounts are quickly flushed from the body. Therefore, taking too much collagen is not dangerous, though it can be wasteful.

When taking collagen supplements, it is important to have adequate Vitamin C and lysine in the diet. Some contain Vitamin C, since it is responsible for building collagen in the body and required for collagen to work. Alpha Lipoic Acid is another supplement to consider in tandem with collagen, since it maximizes the effectiveness of Vitamin C in the body. Alpha Lipoic Acid is also an antioxidant that helps to reduce swelling and pain in the joints.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:

















Discussion Comments
I like Youtheory Collagen Advanced Formula Type I, II, and III. Good prices at Costco or on Amazon. It has no glucosamine, just a dash of Vitamin C.
Collagen is a strong protein. The name collagen comes from the Greek kolla meaning glue and suffix -gen denoting producing.
It is important to note that not all collagen supplements are the same. For high grade collagen supplements, such as those derived from native freshwater fish, these collagen supplements have been found to be bio compatible with humans and absorbed into the blood within a few minutes of the gelatin capsule dissolving. These collagen supplements should be taken during or immediately after a meal, and if you have not eaten plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables with your meal, you should take a natural Vitamin C supplement to ensure you get the maximum effect.
I was conned by an ad saying one needs their hydrolyzed collagen just to stay alive, and since then, learned on the net that it is only broken down into several amino acids.
So why not take any whey/soy, etc. protein
supplements, or simply eat more meat, etc.? Collagen in nothing special -- just a rip-off!
A doctor's site says Vitamin C produces collagen. We should be getting more C, as Americans already
get too much acidifying meat/dairy protein.
And Dr. MdDougall says we are starch eaters.
The company didn't even offer a guarantee,
so I only lost more money to crooks. Shame on them!
BioCell collagen is supported by multiple human clinical trials. Unhydrolyzed or native collagen works very differently in that BioCell collagen works through a regenerative mechanism while the native collagen works through an immunological mechanism.
What's the difference between hydrolyzed collagen and UNhydrolyzed Collagen? then of course type I, II and III?
Good grief. All I want is beautiful hair, great youthful skin and for it to be good for me as well, but which one? Straight and clear answers only please.
You mentioned for us 'vain people' that non-glucosamine collagen supplements often contain collagen I, and collagen III is what we should look for in a capsule. Where do we find these sort of capsules with these ingredients or more? Any brand names? Please.
Why is collagen not digested in the stomach?
"Collagen is water soluble, so excess amounts are quickly flushed from the body. Therefore, taking too much collagen is not dangerous, though it can be wasteful."
Thanks, that's what I wanted to know. Collagen supplements here I come!
Post your comments