At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are Coagulation Factors?
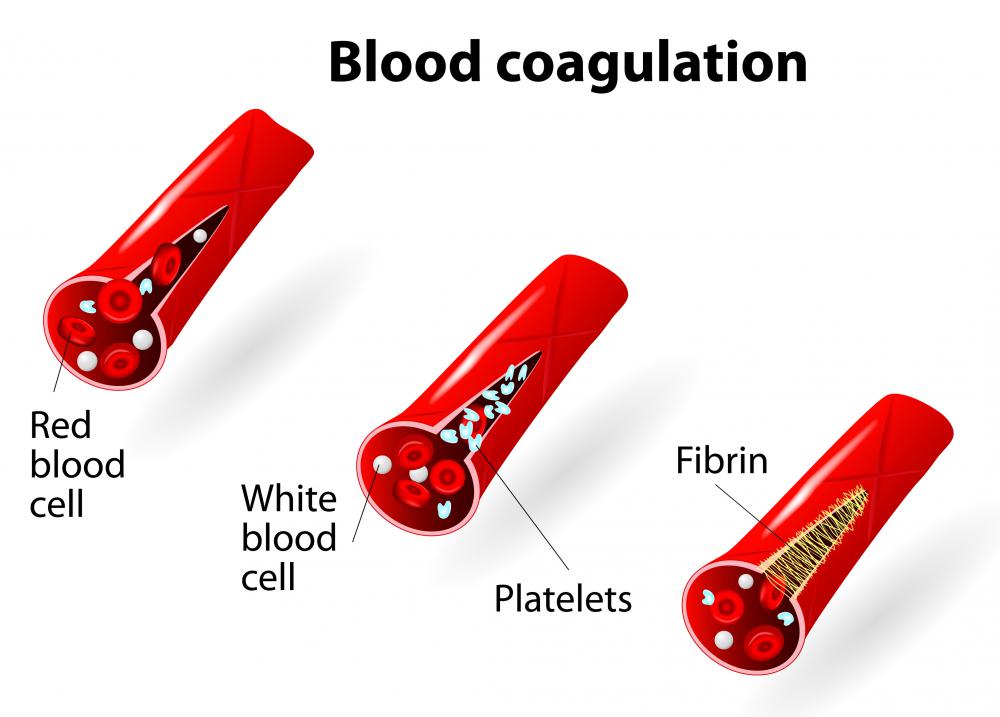
When skin, the organ that provides a continuous barrier for the internal body against the outside world, suffers a discontinuity, a wound is formed. Such openings may be the result of a multitude of events and may vary from unnoticeable to life threatening. The body takes a number of immediate steps to ensure that this opening is closed, or clotted, in order to prevent the loss of blood. There are chemical compounds involved in this complex process, known as coagulation factors.
The clotting of the blood, also known as coagulation, is part of the prevention of blood loss, often termed hemostasis. If this process were to work improperly, as it often does, a person's life may be threatened due to the necessity of proper vascular function and fluid dynamics. On some occasions, a body, due to genetic disease or acute malfunction, may overly compensate for a wound, which may lead to a dangerous clot. In other instances, a person may be physiologically compensated and unable to bridge the gap in the skin. This process takes place instantaneously after a wound is created via external and internal pathways.

The coagulation factors and cofactors work together, often in succession with one chemical combining with others to activate the next. This results in a chain of events geared toward generating thrombin. The coagulation factors' roles in generating thrombin are important, as thrombin is the key substance used in clotting.
There are 13 coagulation factors and a number of related substances involved in hemostasis. Factor I is fibrogen, which aids in clotting. Factor II, or prothrombin, is utilized for the activation of other factors in the chain of events. Tissue thromboplastin and ionized calcium make up Factors III and IV, respectively.

Factors V, VI, and VII refer to proaccelerin, Va, and proconvertin. The prefix pro refers to a precursor, or a molecule that is a substrate in the creation of another. Factor A, which technically speaking is the eighth coagulation factor, is also known as the antihemophilic factor. Factors IX, X, XI, and XII are all activators of other factors and compounds.

Factor XIII is the last recognized factor officially and is known as the fibrin-stabilizing factor. A number of cofactors and associated substances also exist, including fibronectin, heparin cofactor, several proteins, and numerous others. The coagulation factors and cofactors are a very important part of the hemostasis puzzle, but they must be thought of as a part of the machine. Without them, the process could not be successful, but they are also not solely responsible for clotting and blood regulation.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments