At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
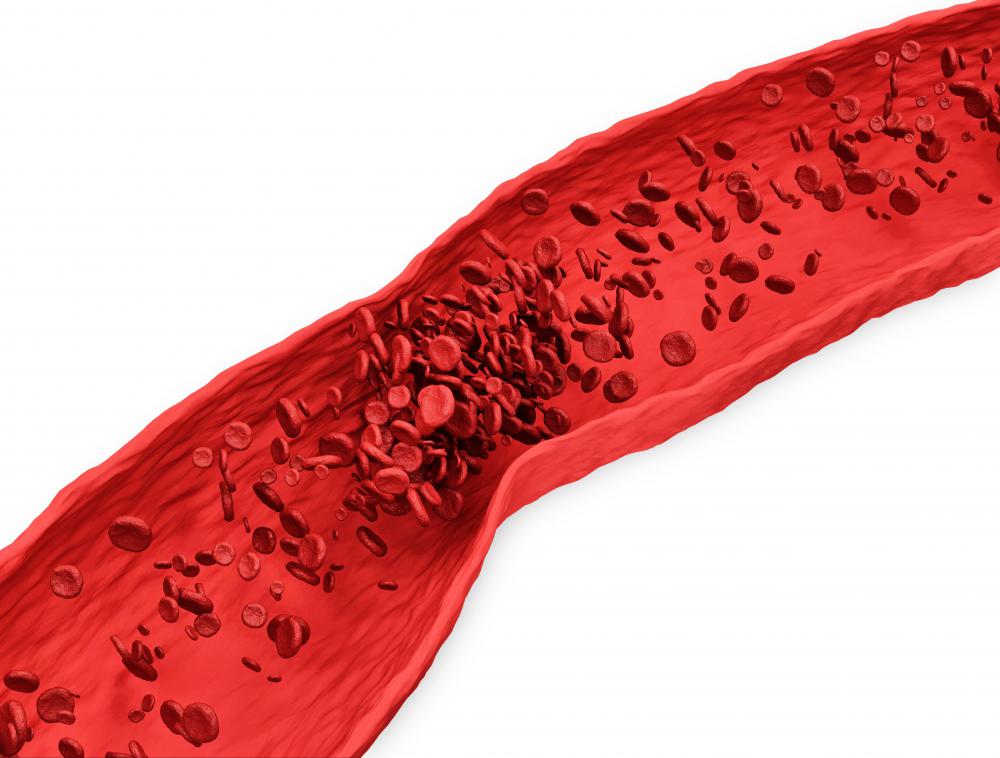
A pulmonary embolism is the sudden blockage of a pulmonary artery, or an artery that supplies the lung. The blockage is commonly caused by a blood clot that has traveled from elsewhere in the body to the lung, but rarely an air bubble or other obstruction can cause the blockage. A pulmonary embolism can cause low blood-oxygen levels and damage to other organs from lack of oxygen, and it is the cause of death for approximately 60,000 patients in the United States each year.
Common sources of blood clots that can cause a pulmonary embolism are the veins deep within the legs. The blood clots may form there as a result of periods of sedentary activity, such as after surgery, during an illness that requires bed rest, or even during long trips in a car, when the legs are not moving. Damage to the veins, as with surgery or an injury can also cause blood clots. In some cases, genetics causes a person's blood to coagulate and form clots.

Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism are often sudden and can include shortness of breath, chest pain when breathing deeply or coughing, and possibly coughing up blood. In some cases, the clot causing a pulmonary embolism is small and the symptoms are more gradual. These gradually occurring symptoms include lightheadedness or fainting, rapid breathing, anxiety, and heavy perspiration.

At the time that signs or symptoms of a pulmonary embolism are displayed, a doctor may order tests to diagnose the condition. Typically, an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) and a chest x-ray are among the first tests ordered. An EKG or ECG allows the doctor to measure the rate and regularity of the heart, while a chest x-ray shows the lungs, heart, and arteries. Other diagnostic tests might include an ultrasound and blood work, which measures the levels of oxygen in the blood.

Many people who have small pulmonary embolisms are immediately placed on an anticoagulant, which is a blood-thinning drug. The drug may be in the form of a pill, an injection, or an IV drip. A large, severe pulmonary embolism can be life threatening and may require surgery to remove or dissolve the clot.
Patients who have previously had a pulmonary embolism are at a greater risk of developing one again, and the risk also increases as a person ages. Other conditions, such as obesity, poor circulation, and genetic disorders, can increase a person's risk of developing a pulmonary embolism. Routine physicals are important to monitor blood pressure and heart rate, and any signs or symptoms should be discussed with a doctor.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
Any sign of pulmonary embolism, such as chest pain, shortness of breath or bloody cough, particularly after prolonged immobility, should be treated as an emergency.
Post your comments