At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Different Types of Suture Materials?
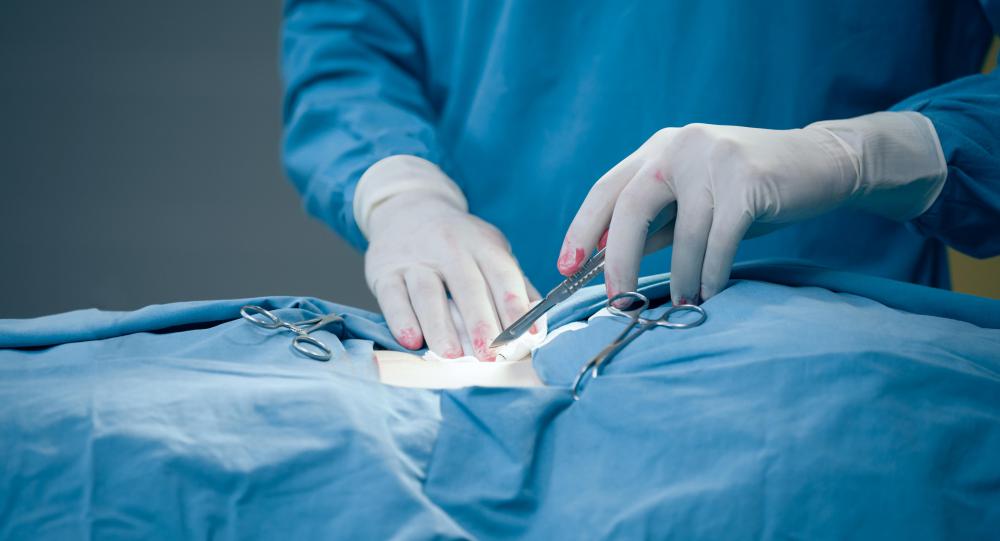
Sutures are rows of stitches that hold together two sides of a surgical incision or wound that is too large to mend on its own. Suture materials are the substances that make up those stitches. There are many different types of suture materials, including both natural and synthetic materials, those that can or cannot be absorbed by the body, and those that are braided or consist of a single strand.
Suture materials are broken down into two main categories: absorbable and non-absorbable. Absorbable sutures are naturally dissolved and digested by the body’s cells and fluids in the area where the sutures are embedded during the healing process. These types of sutures are typically used internally, as it is usually not feasible to bring the patient back in for a second surgery to remove sutures. Non-absorbable sutures cannot be digested by the body and must be removed by a medical professional. They are typically used to repair external cuts and incisions.

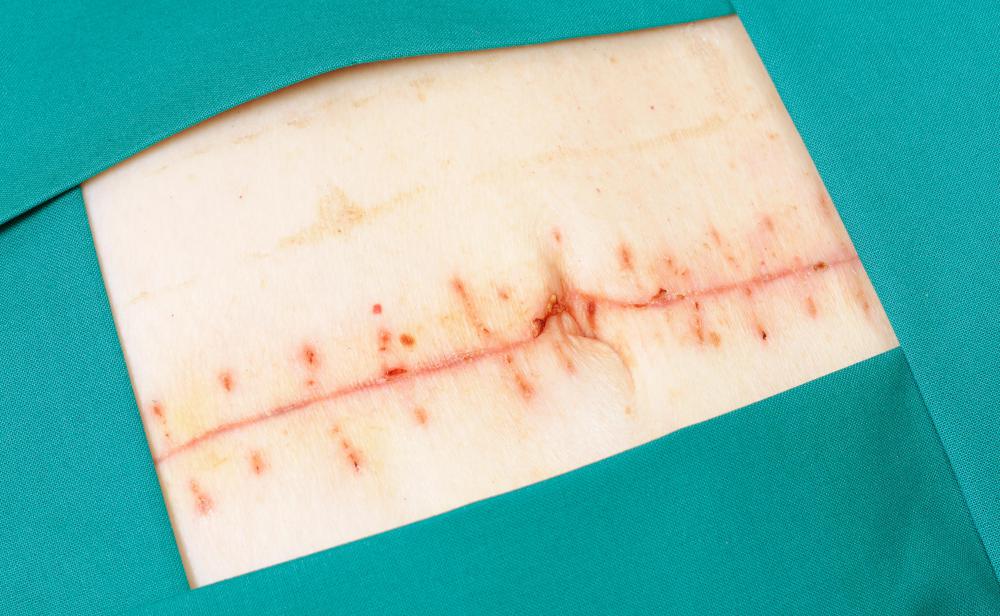
Absorbable suture materials are made from substances that can easily break down in the body’s tissue after a certain amount of time, typically ten days to eight weeks. They were originally made from the intestines of sheep. Later, they were modified and made of specially prepared beef along with the sheep intestines. Some facilities still use these “catgut” materials, although they have been banned throughout Europe and Japan, due to concerns over bovine encephalopathy. Most facilities, however, have moved to using synthetic polymer fiber materials, as they are easier to handle, cost less, and cause fewer reactions in the body’s tissue.

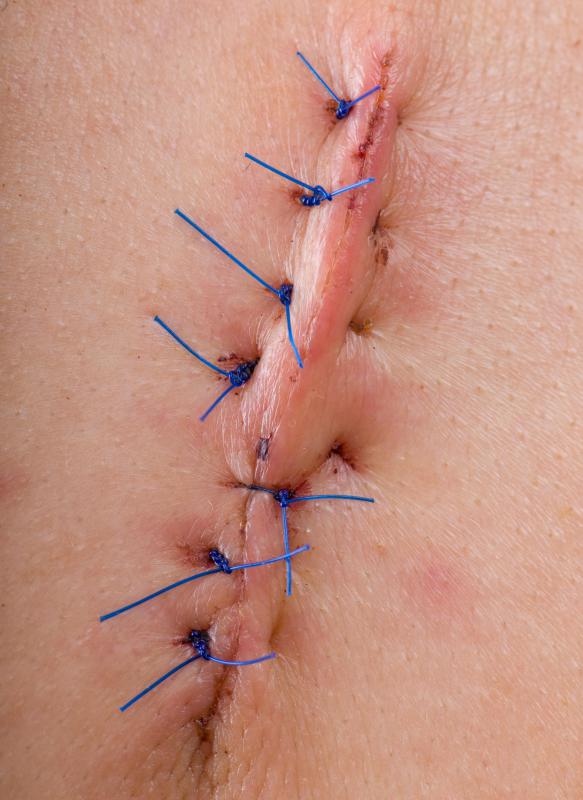
Non-absorbable sutures can be made from numerous synthetic and natural fibers that cannot be metabolized by the body. Silk is the most commonly used of the non-absorbable suture materials. Other materials include artificial fibers such as polypropylene, polyester or nylon, which may have special coatings to make them more efficient. Stainless steel wires may also be used, especially in orthopedic surgery.

Suture materials are also categorized by whether they are multifilament, or braided, or monofilament. Braided materials create a stronger, more secure knot than monofilament sutures, but may cause a more severe reaction in the surrounding tissue. Monofilament sutures are easier to pass through the tissue, but may not be as secure.
With all the different suture materials available, determining the best type for each wound or surgical incision comes down to a matter of the facility’s policy, the doctor’s or surgeon’s expertise, and in some cases, personal preference. Patients should alert the medical staff about any allergies to synthetic or natural fibers, and any complications they may have had in the past with suture materials. To prevent complications, patients should follow all directions regarding care of the sutures.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
This has happened to me twice. The doctor said it was impossible. It has been six months since the procedure, and unfortunately it is on my face.
If you have to have sutures, it is important to talk to your doctor first about the type of material he uses and what you should expect. Many people don't give suture materials much thought, but it definitely pays to know about them if you ever need to have sutures. This knowledge will help you take care of the sutured area and know when to follow up with your doctor if you have any problems or when it comes time to have the sutures removed.
Though absorbable sutures usually dissolve on their own over a certain period of time, I think that it is important that patients know that this is not always the case. For some reason, absorbable sutures take a very long time to dissolve for me, and in the process they often become tight and irritated. My doctor doesn't know why, but said that some peoples' body chemistry just doesn't dissolve sutures very well.
If you have sutures that are absorbable, it is important to keep an eye on them. If they are still in place after the period of time that your doctor said they would dissolve, you should call him with your concerns because he may have to remove them. In the meantime, watch for signs of infection such as warm skin around the sutures, pain in the area, and severe redness of the skin around them.
Post your comments